ADR 0032 - CI Pipeline
Author |
Gabriel Saratura |
|---|---|
Owner |
Schedar |
Reviewers |
|
Date Created |
2025-05-22 |
Date Updated |
2025-05-22 |
Status |
draft |
Tags |
ci,pipeline,cd,github |
|
Summary
Our current CI system no longer aligns with the updated release process, particularly in supporting independent handling of hotfixes and feature requests. The Gitflow workflow has been selected as the branching model for our CI pipeline. |
Problem Statement
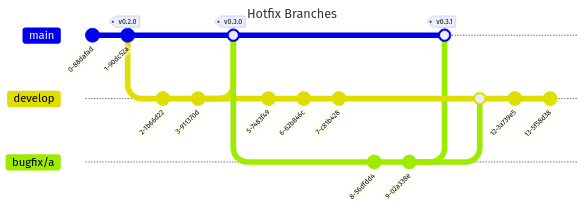
Hotfix Release Cycle
Currently, hotfix pull requests are often entangled with new feature development in the master branch.
This results in the unintended deployment of new features alongside urgent hotfixes.
While this was previously manageable, the recent need to minimize downtime has made this practice unsustainable.
We need a solution that enables hotfixes to be deployed independently, while deferring feature releases to scheduled maintenance windows.
Existing Workflow: Trunk-Based Development
Trunk-based development encourages small, frequent changes merged directly into a central master branch.
This model promotes rapid integration and minimizes merge conflicts, which aligns well with continuous integration goals.
However, the current approach is proving problematic for handling hotfix releases under our new CD process.
Attempted Hotfix Solutions
Forking hotfixes from tags instead of master:
-
No change needed to current CI.
-
Ensures hotfixes are isolated from ongoing feature work.
-
Requires hotfixes to be merged back into
masterlater. -
Tags can be difficult to track and manage effectively.
-
Risk of deploying a tag that lacks the latest hotfix.
Using feature flags in AppCat:
-
High implementation cost.
-
Adds complexity to the AppCat framework.
-
Treats a CI pipeline problem as an application concern—violates separation of concerns.
Proposed Workflow: Gitflow
Gitflow is a branching strategy that separates feature development, hotfixes, and production releases. It introduces distinct branches for features, releases, and hotfixes, which better supports controlled deployments.
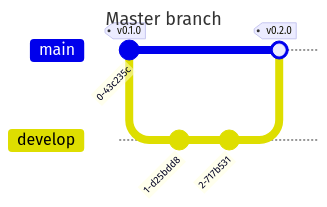
master Branch
-
Represents production-ready code.
-
All production tags originate here.
-
No direct development occurs on this branch.
-
Hotfixes and release-ready features are merged into
master.
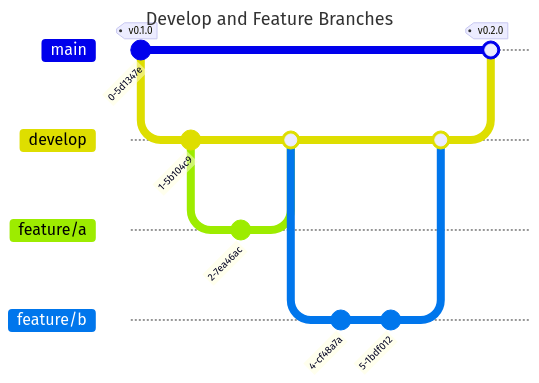
develop and Feature Branches
-
All new features branch off from
develop. -
Once a feature is complete and tested, it is merged back into
develop. -
Features are promoted to
masteronly during planned releases.
Decision
Adopt the Gitflow model and update the CI pipeline accordingly:
-
Create hotfix branches from
masteras needed. -
Merge hotfixes into both
masteranddevelop. -
Use
developfor all ongoing feature work. -
Merge
developintomasteronly during release cycles.
Trade-offs:
-
More complex CI configuration.
-
Clean separation of emergency and planned releases.
-
Solves current pain point with minimal risk of feature leakage during hotfixes.